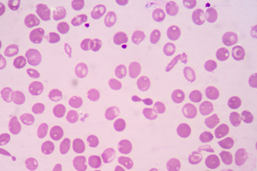
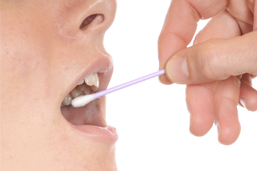
Beta Thalassemia Test (HBB Genotyping)
Find out if you are at risk
- Beta (β) thalassemias are a group of inherited blood disorders
- Defects in the HBB gene cause β-thalassemia
- 60-80 million people around the world carry a β-thalassemia mutation, making it the most common autosomal recessive disorder in the world
- Simple mouth swab DNA test with results in 1 – 2 weeks

What is Beta Thalassemia (HBB) Genotyping?
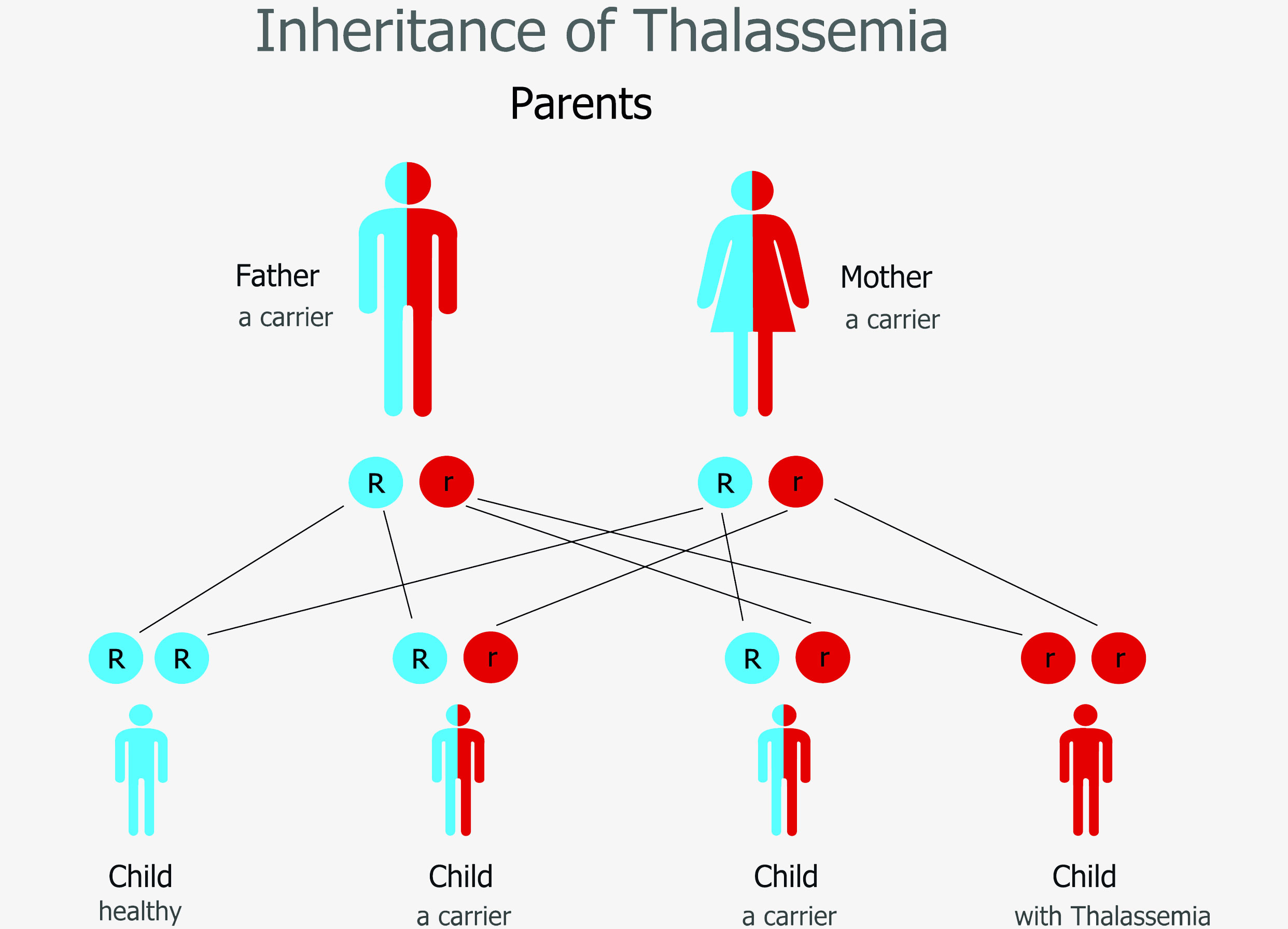
The HBB gene encodes for the β-globin chain of hemoglobin, an essential protein found in red blood cells. Mutations in the HBB gene lead to blood disorders, including β-thalassemia. β-thalassemia is an autosomal recessive disorder, which means two defective copies of HBB are necessary to be affected by the disease. HBB mutations are referred to as either beta-zero (β0), where no β-globin is produced, or beta-plus (β+), where some β-globin is still produced. The severity of β-thalassemia symptoms varies depending on the nature of these inherited genetic change:
- β-thalassemia minor – These individuals have only one defective copy of HBB (either β0 or β+) and are known as carriers of β-thalassemia.
- β-thalassemia intermedia – A condition where individuals have two defective copies of HBB, but at least one copy has a β+ mutation, hence some β-globin is still produced. Symptoms range from mild to severe depending on the amount of β-globin produced.
- β-thalassemia major – Affected individuals have two defective copies of the HBB gene, both with β0 mutations, hence no β-globin is produced. These people experience the life-threatening symptoms of beta thalassemia, including severe anemia, hypochromic (paler than normal) and microcytic (smaller) red blood cells.
Step-by-Step
The kit can be ordered online, by fax or mail, or by phone. Once you place the order, the testing kit will be shipped directly to you. The kit contains swabs called “buccal swabs”. DNA is collected quickly and easily by rubbing the swabs inside your mouth against the cheek for 30 seconds. Once the DNA is collected, the swabs are placed into the specimen container provided in the kit and returned to the laboratory for testing using the return package included in the testing kit. Once your samples arrive at the laboratory, testing begins immediately and results are available in 1 to 2 weeks.
Symptoms of β-Thalassemia
β-thalassemia Major (aka Cooley’s Anemia)
β-thalassemia major is the most severe form of beta thalassemia and is fatal without treatment. Individuals with β-thalassemia major produce no β-globin, resulting in very low levels of hemoglobin, leading to a lack of oxygen in many parts of the body. β-thalassemia major is characterized by:
β-thalassemia Intermedia
β-thalassemia intermedia presents with symptoms that are generally milder than β-thalassemia major. Individuals with this form of thalassemia produce lower levels of β-globin. Underproduction of β-globin also leads to lower hemoglobin levels. β-thalassemia intermedia symptoms vary between individuals and can include:
Frequently Asked Questions
Get Started
Beta Thalassemia Learning Center
How is Beta-Thalassemia treated?
Treatment for beta-thalassemia varies depending on the severity of the disorder. People with beta-thalassemia major and intermedia should be monitored through regular hematological evaluations. During pregnancy, illness or infection, there is a higher chance of [...]
How is Beta-Thalassemia diagnosed?
Beta-thalassemia is diagnosed using genetic testing and blood tests. Genetic testing DNA testing of the HBB gene can be used to diagnose beta-thalassemia. The beta-thalassemia DNA test detects the most common HBB genetic mutations known [...]
What are the signs and symptoms of Beta-Thalassemia?
The signs and symptoms of beta-thalassemia can vary in severity depending on the extent of HBB gene deficiencies. The severity of the disease is classified into three types in the order of decreasing severity: β-thalassemia [...]